While we read all about fungal infections, it should not come as a surprise to some that the antibiotics doctors prescribe as life savers get produced by fungi and certain types of soil bacteria. In a way, nature has been experimenting in her lab through umpteen ways to turn out a lot of powerful and practical survival tools. These tools, as long as they are in place, have proved a blessing to ourselves and our natural ecosystems. Nevertheless, at times they fall out and are all over the place. When that happens, one of the repercussions translates as fungal infections.
To understand what fungal infection is, let us see what fungi are in the first place-All about fungal infections.
It is a general term to signify a broad class of spore-producing organisms feeding on organic matter, including moulds, yeast, mushrooms, and toadstools. The three types of fungi that cause fungal infections
- Moulds
- Yeasts
- Mushrooms
What do they look like
Spot them in three basic shapes:
- Unicellular yeasts,
- Filamentous hyphae (moulds),
- Flagellated, swimming, unicellular organisms that encyst to form sporangia.
How do fungi that cause fungal infections digest food?
All about fungal infections
It digests food externally and absorbs nutrients directly through its cell walls. The young ones of fungi are called spores and have a body (thallus). They are composed of microscopic tubular cells called hyphae. Fungi get classified as heterotrophs and, like animals, obtain their carbon and energy from other organisms.
What are fungal infections?
All about fungal infections.
There are no standard rules for fungal infections. It can happen on the inside of a body as much as on the outside. It can affect anyone, and it can appear on several parts of the body. Their cell walls get made of a fibrous substance called chitin. In some instances, fungi alien to your body internally or externally may still prey on it and cause an infection. An immunity-compromised scenario can multiply out of control and cause an infection.
How does one get infected with a fungal infection?
Fungal infections generally are contagious. They spread through physical contact or through infected spores inhaled. You could sometimes catch disease-causing fungi through infected animals or contaminated soil or surfaces.
If you develop classic symptoms of a fungal infection, make an appointment with your doctor.
What is the life cycle for fungal infection?
Most of the moulds class of fungi go through a four-stage life cycle:
- Spore.
- Germ.
- Hypha.
- Mature Mycelium.
Generally speaking, fungi have a brief life span. However, it differs significantly from species to species. Some types may survive as short as a day, while others linger between a week and a month. Fungus comes into being as a spore and lasts until germination.
What are the many types of fungal infections around?
Fungal infection is also gets known as mycosis. Most fungi are not of any harm to humans, but some of them are capable of causing diseases under specific conditions.
Common types around-All about fungal infections.
Athlete’s foot
The infection gets caused by a group of fungi classified as dermatophytes capable in the warm and humid areas between your toes. It is also known as tinea pedis. It’s one of the types of fungal infections that can affect the skin on your feet, hands and nails.
It’s common among athletes and can spread from one person to another. Contaminated public utilities like a public shower or locker can
be a source.
Symptoms
You will experience the following symptoms between your toes or other parts of your feet
- Itching,
- Stinging,
- Cracking
- Peeling
- Blistering
- A burning sensation
Diagnosis
Your doctor may primarily recognize an athlete’s foot by validating the symptoms on your skin. If in doubt, he may require the affected area to get scrapped, and the skin tested for the fungus.
Jock itch-All about fungal infections.
Jock itch is clinically known as tinea cruris. It’s a fungal infection that settles on your groin area, inner thighs, and buttocks. Like athlete’s foot, the fungal infection caused by dermatophytes tends to thrive in warm and humid regions.
Symptoms
Common jock itch symptoms include:
- a burning feeling
- changes in skin colour
- flaking or cracking skin
- a rash that gets worse when you exercise
- redness
- itchiness
Diagnosis
If clinical diagnosis fails to confirm its presence, a pathological test may require scraping skin cells and examining them.
Ringworm-All about fungal infections.
Ringworm fungal infections affect your skin and scalp. They, too, get classified under dermatophytes. Ringworms grow on the skin; they thrive in damp and humid parts of your body.
Symptoms
It usually manifests as a reddish, itchy, scaly rash. In time, patches of ringworm can spread and form red rings.
Other signs include:
- Patches that resemble rings with a redder outside edge
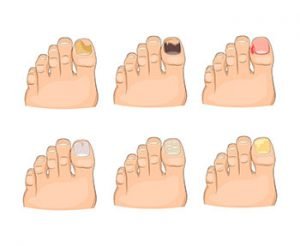
- Thick, discoloured, or cracked nails (if the infection is in the nails)
- Patches that host blisters and start to ooze
- Bald patches on the scalp
Diagnosis
The doctor will shine a black light over the affected area to confirm the infection. On second thought, he will require a sample of the affected skin to be scrapped and sent for lab verification.
Yeast infection-All about fungal infections.
Candida albicans or yeast infection is a fungus that can infect your skin, mouth, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, or genitals.
It is usual for small amounts of candida Albicans to be always present on your skin and in your body. But when these fungi begin to exceed too much, it qualifies as a yeast infection.
Symptoms
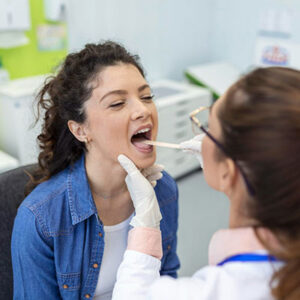
Oral thrush is when you get infected with yeast infection in your throat or mouth. Its typical onset gets verified by the white patches formed in your mouth and throat. People with prolonged antibiotic therapy often are at high risk of infection.
Vaginal yeast infections are common among women. They can cause:
- clumpy discharge
- swelling
- redness
- pain
- itchiness
Diagnosis
To check for oral thrush, your doctor will perform a few throat swabs to get sent to a lab, where technicians will culture them to learn the nature of fungi.
What are the most vulnerable conditions making one prone to fungal infections?
Many things can put you at risk of developing a fungal infection. Environmental factors play a significant role, but your body’s condition will also decide the extent of disease you will have post-exposure.
Dampness and humidity
Maintain personal hygiene. A warm and moist environment is pertinent for fungi to thrive. So if you sweat a lot or work in a hot or humid environment, you need to be on the watch.
Walking barefoot in damp places can also trigger an infection as public spaces are often rich in fungal spores.
Poor blood circulation
Poor quality of blood circulation can raise your risk of infection. Poor circulation lingers your immune response and decreases your body’s ability to fight off an infection.
Menopausal status-All about fungal infections.
Hormonal changes in postmenopausal women can reduce the acidity of your vagina, making you vulnerable to vaginal yeast infections.
Suppressed immune system
A suppressed immune system is an open invitation making you vulnerable to fungal infections.
Nutrient deficiencies, immunodeficiency disorders, smoking, and stress can impair your immune function.
Nail and skin injury or infection
A small nail or skin injury could get infectious, attracting fungi under your skin and affecting deeper tissues. Hence it’s imperative to wash wounds and cover them in a sterile dressing.
Certain medications
Certain medications doze off your body’s ability to ward off fungal infections. Antibiotics don’t differentiate between good or bad bacteria. They destroy both. So fungi get the liberty to thrive, free of natural opposition.
Prolonged use of corticosteroids will increase your risk of fungal infection. Cancer treatments, especially chemotherapy and radiation, will increase the risk of catching similar conditions.
How should one guard against fungal infections?
Tips to avoid fungal infections
1 Wear clean and dry clothes.
The common habit of people reusing their clothes a few times before they wash them can make them prone to fungal infections. Make it your habit to wear clean and dry clothes, especially undergarments and socks.
2 Avoid wearing tight clothes and shoes.
Sweat and dampness is the ideal environment for fungus to thrive. Allow your skin to breathe well. It will help keep your body getting sweaty and damp. Avoid tight-fitting clothes and shoes.
3 Bathe at least once a day.
The basic tenet of personal hygiene, having it once a day is enough to maintain good hygiene. But, a shower is most advisable after gyming or severe sweating. Dry your body entirely after a shower or a bath.
4 Keep your nails trimmed short and clean.
Clean your nails and the area underneath thoroughly while bathing. While short nails help prevent the spread of infection, never cut your cuticles. Never share nail clippers with others, and clean them before and after each use.
5. Keep yourself dry.
As far as possible, Keep your body parts most vulnerable to fungal infections like feet, groins, underarms, and buttocks dry and clean. These are areas most likely to get infected because of lingering dampness. Use breathable material for clothes and shoes, and immediately change wet underwear, socks, or clothes.
6. Check if anyone in your family member has a fungal infection.
If anyone in your family displays a fungal infection, let the person see a dermatologist immediately. Stop sharing clothing and other personal items such as combs with anyone, as this could spread the infection. Wipe and disinfect shared surfaces with a disinfectant.
7. Avoid being barefoot.
Wearing sandals or flip-flops can be a barrier, especially in common areas such as locker rooms and gyms. You can avoid catching fungal infections from the floor with cuts on your feet.
8 Look after your diet.
Probiotics (foods with live bacteria beneficial to your health) to your diet can help your body fight against the harmful fungi that cause infections.
Cut down sugar consumption as it increases the risk of yeast infections. Remaining embarrassed or secretive about fungal infections can worsen their onset. They are treatable and manageable. So seek medical help at the earliest spotting symptoms of a fungal infection.
Natural kitchen remedies available against fungal infections
1 Consume Yoghurt and Probiotics
Yoghurt, Fermented foods, probiotics and other probiotic supplements have a high concentration of good bacteria that help fight harmful bacterial and fungal infections.
2 Wash with Soap and Water
Washing with soap under flowing water helps to keep the spread down and lowers the intensity of the infection.
3 Use Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has significant antifungal properties. Mix two tablespoons in warm water and have it. Alternatively, you could dip a cotton ball in it and dab it over your skin. Do it at least thrice a day to see faster results.
4 Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is full of antifungal and antibacterial properties. It is a highly effective home remedy to treat fungal infections. Combine it with any coconut oil, olive oil, or other carrier oil and dab over the infected area thrice a day.
5 Use Coconut Oil
To exploit it as a potent antifungal agent, use it in its unheated form. It is topically effective and safe. Apply it thrice a day to get rid of scalp ringworm.
6 Use Turmeric
It is a proven antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory spice. It is one of the most accessible home remedies for fungal infections. Make a paste of it by mixing it with a bit of water. Apply over the infected area. You can also consume it with warm water or have turmeric tea.
7 Use Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has been around since the dawn of humans and is thoroughly time-tested to be a natural remedy for skin infections. It is perfect for treating the condition while collaterally soothes and repairing skin damage.
8 Garlic
Those who eat garlic regularly will be least susceptible to fungal infections due to its potent antifungal and antimicrobial herbs. Mix Garlic paste with some olive oil for topical use. Generously apply to the infected area several times a day for fast turnaround.
9 Oregano Oil
Oregano oil is also an active antifungal agent. Pour a few drops into a carrier oil and dab frequently on the affected area. Orally ingesting oregano oil capsules will also help in initiating fast healing.
However, check for any oil allergies before you use them.
10 Neem Leaves
The antifungal properties of neem leaves are highly effective and are extremely good for the skin. Boil Neem water first and let it cool before washing the infected area with it for about 2 to 3 minutes.
11 Consuming foods rich in Vitamin C
Vitamin C or ascorbic acid invigorates our immune system. It protects our body by fighting off various infections.
12 Baking Soda
Baking soda helps keep away fungal infections like athlete’s foot. Regularly apply baking soda powder on the feet and the inside of shoes to absorb moisture and sweat. Nip the disease from spreading.
13 Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen Peroxide helps heal the Athlete’s Foot. Soak your feet in an equal parts solution of water and hydrogen peroxide as it effectively kills the fungus causing athletes’ feet.
14 Ginger
Gingerol inherent in ginger has potent antifungal properties. Making ginger a part of our diet as ginger tea helps prevent and treat fungal infections like Candida.
15 Honey
Honey contains hydrogen peroxide and which makes it effective against fungal infections. Apply raw honey to the affected region thrice daily and see the healing occur after some days.
16 Grapefruit Seed Extract
Research proves that grapefruit seeds extract can be used to treat fungal infections. Extract a drop of the seed, mix it with a few drops of water, and apply it to the sore spot twice a day.
17 Powdered Liquorice
Liquorice is naturally endowed with anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial properties to tackle fungal infections. Use powdered liquorice by adding it to a cup of water and boil. After a few minutes, allow it to simmer. Once you get a paste-like consistency, let it cool. Later apply the mixture to the affected skin twice a day.
18 Lemongrass oil
Lemongrass, laden with antimicrobial properties, is easy to use as one of the home remedies. Mix lemongrass oil with carrier oil, dab it on the affected region with a cotton ball or swab twice a day.
Conclusion
Fungus is not harmful if it coexists peacefully. The need to get rid of it arises when it gets found encroaching on our private spaces. Don’t unwittingly invite them. Wear your hygiene to the mark and fungi will only be too happy not to intrude.
1. What happens to fungal infection if left untreated?
It will rarely subside on its own. More likely, it may lead to serious health issues, such as skin infections, fatigue, and oral thrush.
2. Are all fungal infections contagious?
Yes, it can be so in some cases. Don’t take chances. They have the potential to spread and infect. You must consult a doctor if you develop signs or symptoms of a fungal infection.
3. Do fungal infections spread more in winter?
Yes, winters are particularly damp, a perfect environment for most fungal infections to break out. Ensure that you always leave your skin clean and dry, as even a little sweat can trigger a fungal condition.
Disclaimer
The information mentioned herein is not a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional. Individual needs will always be unique. Hence readers should exercise discretion and consult their physician to determine the appropriateness of the information for a given situation.